Prostate Segmentation
3D Prostate Segmentation from MR Images using FCNN
- Prostate cancer is among the most commonly diagnosed and leading causes of cancer related death in developed countries.
- The early detection of prostate cancer plays a significant role in the success of treatment and outcome.
- Radiologists first segment the prostate image from ultrasound image and then identify the hypoechoic regions which are more likely to exhibit cancer and should be considered for biopsy.
- Manual segmentation consumes considerable time and effort and is not only operator-dependent, but also tedious and repetitious.
- In this work we present an appraoch to segment prostate using Fully Convolutional Neural Networks without requiring the involvement of an expert.
- We were able to obtain results comparable to the state-of-the-art, with the average Dice loss of 0.92 and 0.80 on train and validataion set respectively.
Data
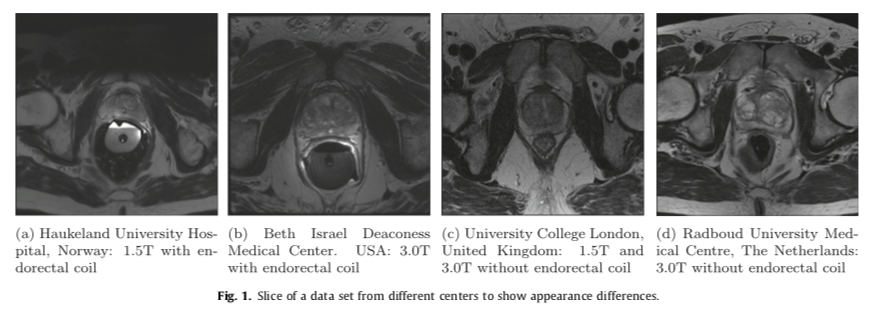
- In MRI images, the voxel intensities and therefore appearance characteristics of the prostate can greatly differ between acquisition protocols, field strengths and scanners.
- Therefore a segmentation algorithm designed for use in clinical practice needs to deal with these issues.
- We decided to use the data from PROMISE12 challenge which included the scans from four different centers
- Haukeland University Hospital (HK), Norway
- Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), United States
- University College London (UCL), United Kingdom
- Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre (RUNMC), Netherlands.
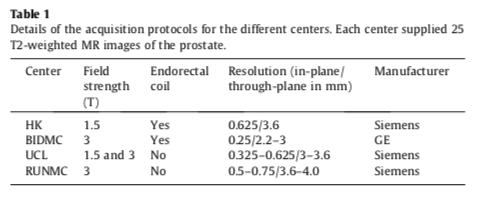
- Each of the centers provided 25 transverse T2-weighted MR images. This resulted in a total of 100 MR images.
- Details pertaining to the acquisition can be found in the table below.
Implementation
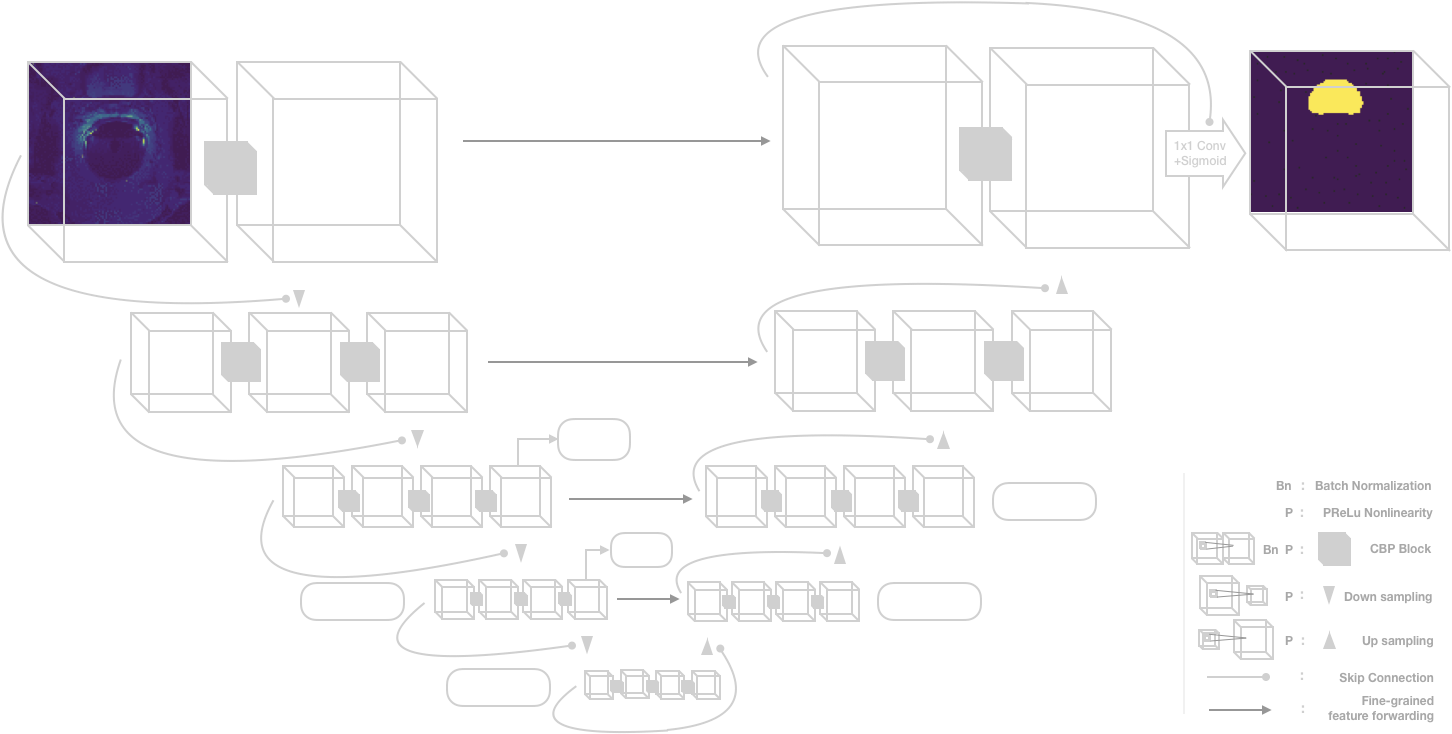
We used a modified V-net architecture for segmentation that is shown below.
Training
We trained our model on different GPUs and got the following speedups.
| GPU configuration | Batch Size | Average Time per Epoch (s) |
|---|---|---|
| Single K80 | 2 | 147 |
| Dual k80 | 2 (1 per GPU) | 102 |
| Single P100 | 2 | 48 |
| Single P100 | 5 | 27 |
Evaluation Metrics
The metrics used in this study are widely used for the evaluation of segmentation algorithms:
- Dice coefficient: To measure the similarity between output volumes.
- Absolute relative volume difference: the percentage of the absolute difference between the volumes.
- Average boundary distance: the average over the shortest distances between the boundary points of the volumes.
- 95% Hausdorff distance: the maximum of the shortest distances between the boundary points of the volumes. 95% percentile makes the metric less sensitive to outliers.
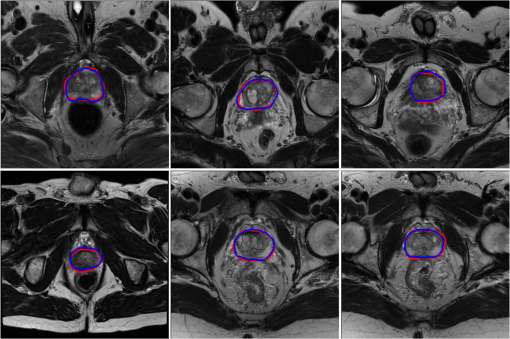
Results
After training for 5700 epochs we got a dice loss of 0.94 and 0.87 on training and validation set. The results were then submitted to the MICCAI PROMISE12 challenge, and we received a score of 84.61 on the test set.